Which Of The Following, Cetreis Paribus, Would Increase The Money Supply?
eighteen.9 Effects of a Money Supply Increment
Learning Objective
- Acquire how a change in the money supply affects the equilibrium interest rate.
Expansionary monetary policyAn increase in the money supply in a land. refers to any policy initiative by a state'due south central bank to raise (or expand) its coin supply. This tin be achieved with open market purchases of government bonds, with a decrease in the reserve requirement, or with an announced decrease in the discount rate. In near growing economies the money supply is expanded regularly to keep up with the expansion of gross domestic product (GDP). In this dynamic context, expansionary monetary policy can mean an increase in the rate of growth of the money supply, rather than a mere increase in money. However, the money market model is a nondynamic (or static) model, and then we cannot hands incorporate coin supply growth rates. Nonetheless, we tin project the results from this static model to the dynamic earth without much loss of relevance. (In contrast, any decrease in the money supply or decrease in the growth rate of the money supply is referred to as contractionary monetary policy.)
Suppose the money market is originally in equilibrium in Figure 18.3 "Effects of a Money Supply Increase" at bespeak A with real money supply M Due south ′/P $ and interest charge per unit i $′ when the money supply increases, ceteris paribus. The ceteris paribus assumption means we assume that all other exogenous variables in the model remain fixed at their original levels. In this practise, it means that real Gdp (Y $) and the price level (P $) remain fixed. An increase in the coin supply (K Southward ) causes an increment in the real money supply (Grand S /P $) since P $ remains constant. In the diagram, this is shown equally a rightward shift from One thousand Southward ′/P $ to Thousand S ″/P $. At the original interest charge per unit, real money supply has risen to level two along the horizontal centrality while real money demand remains at level 1. This means that money supply exceeds money need, and the actual involvement rate is higher than the equilibrium charge per unit. Adjustment to the lower interest charge per unit will follow the "involvement rate also loftier" equilibrium story.
Figure eighteen.3 Furnishings of a Money Supply Increase
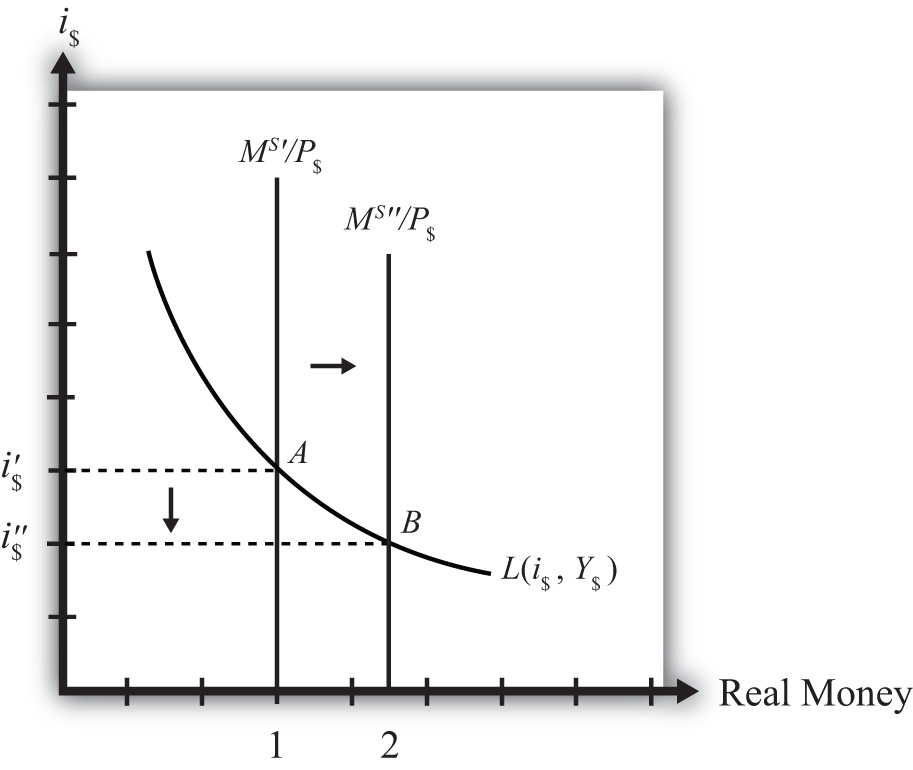
The last equilibrium will occur at indicate B on the diagram. The real money supply volition have risen from level 1 to two while the equilibrium interest rate has fallen from i $′ to i $″. Thus expansionary monetary policy (i.e., an increase in the money supply) will cause a decrease in average interest rates in an economy. In dissimilarity, contractionary monetary policy (a decrease in the coin supply) will cause an increase in average interest rates in an economy.
Note this outcome represents the curt-run issue of a money supply increase. The brusk run is the time before the money supply tin touch the cost level in the economy. In Chapter 18 "Interest Rate Determination", Department 18.14 "Money Supply and Long-Run Prices", we consider the long-run effects of a coin supply increase. In the long run, coin supply changes can touch on the price level in the economic system. In the previous exercise, since the price level remained fixed (i.eastward., subject to the ceteris paribus assumption) when the money supply was increased, this exercise provides the curt-run outcome.
Cardinal Takeaway
- An increment (decrease) in the money supply, ceteris paribus, will cause a decrease (increment) in average interest rates in an economy.
Exercise
-
Jeopardy Questions. As in the popular boob tube game show, you are given an answer to a question and you must respond with the question. For example, if the answer is "a revenue enhancement on imports," and then the right question is "What is a tariff?"
- Term often used to describe the type of budgetary policy that results in a reduction of the money supply.
- Term often used to describe the type of monetary policy that results in an increase in the coin supply.
- Of increase, decrease, or stay the same, the effect on the equilibrium interest rate when the nominal money supply increases, ceteris paribus.
- Of increment, decrease, or stay the same, the consequence on the equilibrium involvement rate when the nominal coin supply decreases, ceteris paribus.
- Term for the fourth dimension period before price level changes occur in the coin market model.
Source: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_international-economics-theory-and-policy/s21-09-effects-of-a-money-supply-incr.html
Posted by: mcgaughcaut1994.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Of The Following, Cetreis Paribus, Would Increase The Money Supply?"
Post a Comment